What are the components of leather dyes? How is leather dyed?
What are the components of leather dye? How does leather dye color?
A very important prerequisite for using leather dye well in leather dyeing is to first understand leather dye. We need to know what the components of leather dye are, which is very beneficial for successfully achieving dyeing goals and improving dyeing processes. This article will briefly introduce the components of leather dye.
The material components of leather dye include various dyes with different characteristics. They can generally be divided into the following five categories:
1. Dye body: The colored substance that can perform the dyeing function.
2. Semi-dye body: A byproduct of low molecular weight dyes, which is the product of incomplete reactions in the synthesis of leather dye. The characteristic of organic synthesis is that there is no 100% conversion rate, and there will always be some incomplete reactions in the production process.
3. Inorganic salts: Inorganic salts are produced during the chemical reactions in leather dye production, most of which are sodium sulfate, and there is also a process that produces sodium chloride. Inorganic salts are also added during the salting-out process. Sodium sulfate is often added when adjusting dye strength.
4. Additives: Substances added to ensure the excellent use characteristics and quality stability of leather dye, such as strength regulators, surfactants, co-solvents, dispersants, etc. For example, in leather-specific dyes, sodium sulfate is used as a strength regulator, and light-colored dispersants are added. In acidic dyes, sodium sulfate is used as a pressure regulator. If the solubility is low, soda ash can be added, and light-colored dispersants can also be added. When dyeing leather directly, sodium sulfate is used as a strength regulator, and soda ash, disodium hydrogen phosphate, and low-bacterial salt dispersants are added to dyes with low solubility.
5. Impurities: These are impurities contained in the raw materials of leather dye, impurities introduced during the production process, and unreacted raw monomers.
How to color leather with leather dye?
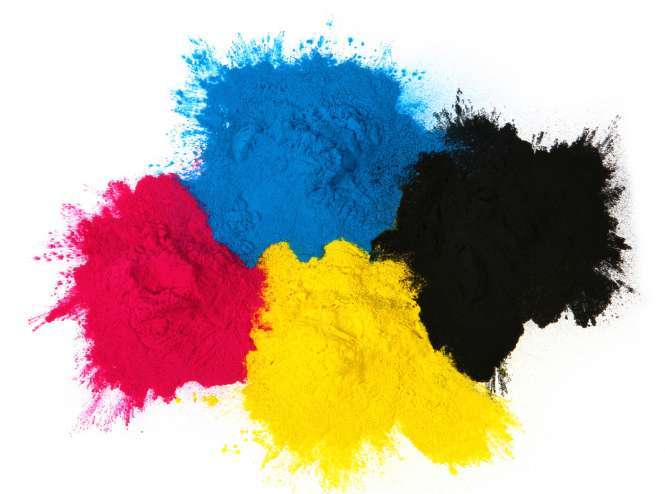
The coloring process of leather generally adopts the basic principle of the color triangle: leather is dyed with one dye, and if the desired color is not achieved, several pigments need to be selected for color matching. For example, by mixing the red and blue parts of the spectrum, purple can be obtained. During color matching, the color of the mixed pigments is determined by the mixed light reflected by various pigments. Currently, there is no perfect color matching standard for leather dyes. However, a considerable amount of practical experience has been accumulated. There are some effective and practical methods for color matching. Following this color matching method, one can quickly master the color matching of some leather dyes. The color matching method based on the basic principle of the color triangle is introduced.
In the subtractive color method, the three primary colors red, yellow, and blue cannot be paired with other colors, but they can be paired with multiple colors. The subtraction of the three primary colors forms a triangular area. Color matching experience: black plus white equals gray, yellow can be added with white and red, light colors can be added with black. The vertices of the triangle are red, yellow, and blue. The center of the triangle has a black area, with an inverted black triangle, and the colors on each side of the triangle are binary colors, which can be added in any proportion of the printing colors of any two of the three printing colors. For example, at the edge of yellow and cyan, some secondary colors can be created, such as lemon yellow, cyan, and yellow; in the secondary colors, moving along the direction of yellow and blue in the triangular color sample will make the color darker.
In addition to primary and secondary colors, the red-yellow-blue triangle also has three other colors. The color at each point in the triangle contains the three primary colors red, yellow, and blue, and black can be mixed with equal amounts of the three primary colors. Additionally, through any straight line in the black area, the colors represented by the two points where the color matching intersects on both sides are basically complementary colors, and these complementary colors can also be blended into black in a certain proportion.
Latest developments